
GMX
GMX 价格
$15.1800
+$0.33000
(+2.22%)
过去 24 小时的价格变化

您感觉 GMX 今天会涨还是会跌?
您可以通过点赞或点踩来分享对该币种今天的涨跌预测
投票并查看结果
免责声明
本页面的社交内容 (包括由 LunarCrush 提供支持的推文和社交统计数据) 均来自第三方,并按“原样”提供,仅供参考。本文内容不代表对任何数字货币或投资的认可或推荐,也未获得欧易授权或撰写,也不代表我们的观点。我们不保证所显示的用户生成内容的准确性或可靠性。本文不应被解释为财务或投资建议。在做出投资决策之前,评估您的投资经验、财务状况、投资目标和风险承受能力并咨询独立财务顾问至关重要。过去的表现并不代表未来的结果。您的投资价值可能会波动,您可能无法收回您投资的金额。您对自己的投资选择自行承担全部责任,我们对因使用本信息而造成的任何损失或损害不承担任何责任。提供外部网站链接是为了用户方便,并不意味着对其内容的认可或控制。
请参阅我们的 使用条款 和 风险警告,了解更多详情。通过使用第三方网站(“第三方网站”),您同意对第三方网站的任何使用均受第三方网站条款的约束和管辖。除非书面明确说明,否则欧易及其关联方(“OKX”)与第三方网站的所有者或运营商没有任何关联。您同意欧易对您使用第三方网站而产生的任何损失、损害和任何其他后果不承担任何责任。请注意,使用第三方网站可能会导致您的资产损失或贬值。本产品可能无法在所有司法管辖区提供或适用。
请参阅我们的 使用条款 和 风险警告,了解更多详情。通过使用第三方网站(“第三方网站”),您同意对第三方网站的任何使用均受第三方网站条款的约束和管辖。除非书面明确说明,否则欧易及其关联方(“OKX”)与第三方网站的所有者或运营商没有任何关联。您同意欧易对您使用第三方网站而产生的任何损失、损害和任何其他后果不承担任何责任。请注意,使用第三方网站可能会导致您的资产损失或贬值。本产品可能无法在所有司法管辖区提供或适用。
GMX 市场信息
市值
市值是通过流通总应量与最新价格相乘进行计算。市值 = 当前流通量 × 最新价
流通总量
目前该代币在市场流通的数量
市值排行
该资产的市值排名
历史最高价
该代币在交易历史中的最高价格
历史最低价
该代币在交易历史中的最低价格
24 小时最高
$15.2600
24 小时最低
$14.1500
历史最高价
$91.4100
-83.40% (-$76.2300)
最后更新日期:2023年4月18日
历史最低价
$9.5600
+58.78% (+$5.6200)
最后更新日期:2025年4月7日
GMX 动态资讯
以下内容源自 。

ChainCatcher 链捕手
原标题:《What does it mean to be a Hyperliquid-aligned fiat stable?》
作者:husd_fiat
编译:zhouzhou,BlockBeats
编者按:HUSD 是 Hyperliquid 推出的公共稳定币项目,将稳定币利息回流生态,用于回购 HYPE、补贴接口费率、支持 Builder Code 模式,推动生态增长。它打破 USDC/Tether 模式,让资金不再流向中心化机构,而是反哺社区和产品发展。
以下为原文内容(为便于阅读理解,原内容有所整编):
生态系统真正需要的东西
HUSD 的故事,讲的是如何颠覆一个价值数十亿美元的稳定币市场。Hyperliquid 最初是以领先的永续合约去中心化交易所(perp DEX)身份出现的,优于 DYDX 和 GMX 等旧玩家。随着产品持续吸引新用户,并逐步引入现货市场,Hyperliquid 逐渐演变成了一个 Binance / Coinbase 的竞争对手。接下来,生态系统要挑战的对象,是法币稳定币的双头垄断——Circle 和 Tether。
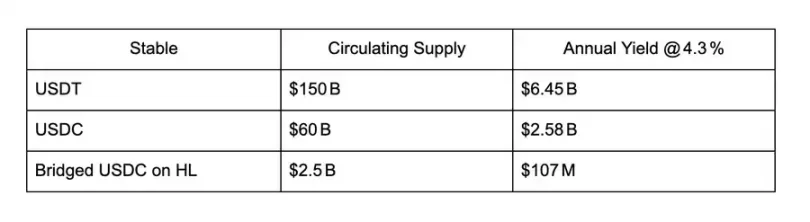
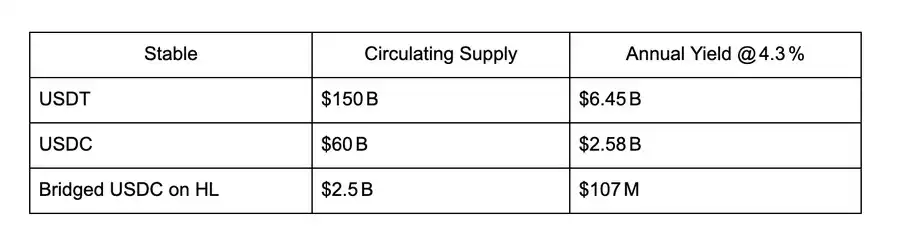
目前,大约有 25 亿美元的跨链 USDC 被锁定在 HyperCore 的订单簿中,并获得约 4.3% 的利息收益。这些收益每年可为 Circle Internet Financial 带来约 1.075 亿美元的收入,流入其私人资产负债表。每一笔新存入 Hyperliquid 的 USDC,都在进一步扩大 Circle 的现金流。但如果这些价值不是流向 Circle,而是反过来用于壮大 Hyperliquid 生态,会怎么样?在有机会突破现有框架的情况下,我们为什么还要被 USDC 这种过时的传统稳定币模式所束缚?
选择沿用旧稳定币的机会成本
随着 Hyperliquid 在链上交易中的影响力不断扩大,法币稳定币的净存款也随之增长,为永续合约市场和现货市场提供流动性。在一个 Hyperliquid 增长 10 倍、100 倍、甚至 1000 倍的未来里,继续使用传统稳定币的机会成本也会越来越高。这些来自稳定币层的价值,要么继续流向 Circle 和 Tether 的资产负债表,要么回流到 Hyperliquid 自身生态中。
为 Hyperliquid 量身打造的新稳定币模型
「援助基金」(Assistance Fund)通过自动回购 HYPE 已经证明:协议产生的现金流完全可以、也应该直接回馈给社区。仅过去 30 天,援助基金就从市场中回收了数百万美元的 HYPE。
HUSD 延续这一策略,只不过它是在稳定币层面展开:一开始,HUSD 所带来的利息收入中,一大部分将用于购买 HYPE,然后把这些 HYPE 再部署到 Hyperliquid 生态的各个增长方向上。换句话说,每一次你使用 HUSD,都会为 HYPE 增加买压,并把价值重新投入 Hyperliquid 的发展中。
被回购的 HYPE 将如何被使用?
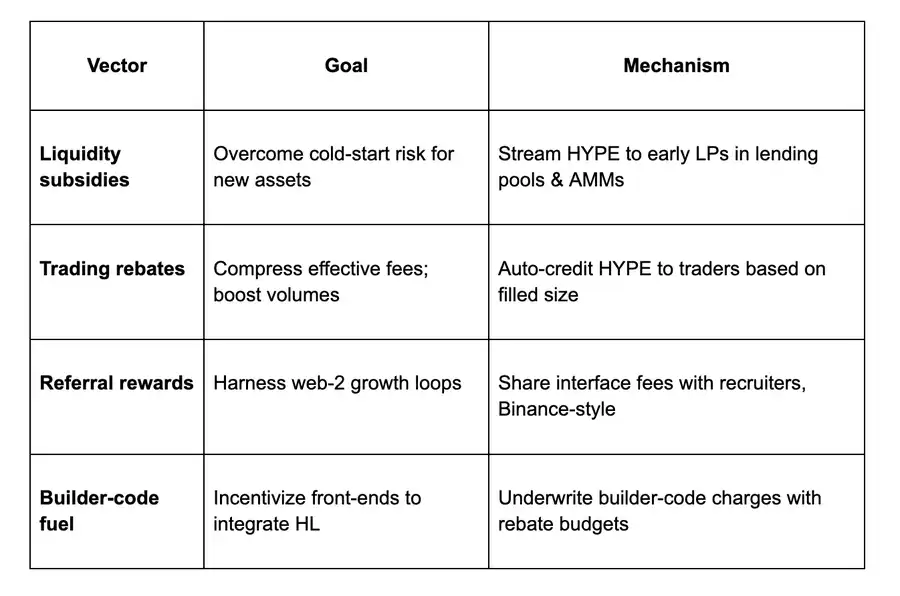
HUSD:为 Builder Code 未来提供燃料
HUSD 在推动「Builder Code」商业模式的爆发中起着关键作用。Builder Code 是 Hyperliquid 的原生功能,允许一个界面运营者(interface operator)在代表用户提交的现货或合约交易中收取一定费用。它的目标是为 Hyperliquid 的「最后一公里分发」提供变现方式——也就是说,任何能有效吸引并留住用户的人,都可以通过 Builder Code 建立起一个不受技术或流动性限制的交易业务。
这类业务的单位经济效益可能非常可观,但在目前这个早期阶段,新品牌仍面临「冷启动」问题,而不同接口之间的护城河也还不明显。HUSD 的出现,可以帮助这些「Hyperliquid 混合体」完成启动,同时提供一种方法让它们之间形成差异化。
通过 HUSD 补贴 Builder Code 的费用,接口可以向用户收取比原本更高的费用,却不增加用户成本。接口能实时获得收入,并进一步将这些资金用于增长策略。
举个例子:假设 Interface XYZ 获得了 100 HUSD 的返利预算。所有带有其 Builder Code 的合约交易都会被系统统计,相应用户的返利余额也会不断增长。在用户真正开始承担费用之前,该接口至少可以处理约 $100,000 的合约交易量(即 100 HUSD 除以 0.1% 的手续费率)。与此同时,接口运营者也可以把 Builder Code 带来的收入再投入到拉新或用户留存中。
这就是 HUSD 为 Hyperliquid 生态「实时增长」提供动力的方式。
总结
HUSD 融合了两个核心洞察:将交易使用的计价资产(稳定币)以及由它产生的现金流,统一纳入交易平台体系内。最终结果,就是一个「公共产品」性质的稳定币,它将原本静态的储备利息,转化为 Hyperliquid 生态的主动式、复利式增长。
HUSD 是一个由 Felix 运营、社区成员支持的公共产品项目,它将通过 Felix Points 系统上线。这一部署也建立在 @m0foundation 打下的基础之上,正是其对「全球稳定币平台」的愿景,才让 HUSD 成为可能。
Hyperliquid 已经颠覆了中心化交易所的格局,而 HUSD 正准备对传统法币稳定币做同样的事。

1.09万
0

Blockbeats
原文标题:What does it mean to be a Hyperliquid-aligned fiat stable?
原文作者@husd_fiat
原文编译:zhouzhou,BlockBeats
编者按:HUSD 是 Hyperliquid 推出的公共稳定币项目,将稳定币利息回流生态,用于回购 HYPE、补贴接口费率、支持 Builder Code 模式,推动生态增长。它打破 USDC/Tether 模式,让资金不再流向中心化机构,而是反哺社区和产品发展。
以下为原文内容(为便于阅读理解,原内容有所整编):
生态系统真正需要的东西
HUSD 的故事,讲的是如何颠覆一个价值数十亿美元的稳定币市场。Hyperliquid 最初是以领先的永续合约去中心化交易所(perp DEX)身份出现的,优于 DYDX 和 GMX 等旧玩家。随着产品持续吸引新用户,并逐步引入现货市场,Hyperliquid 逐渐演变成了一个 Binance / Coinbase 的竞争对手。接下来,生态系统要挑战的对象,是法币稳定币的双头垄断——Circle 和 Tether。
目前,大约有 25 亿美元的跨链 USDC 被锁定在 HyperCore 的订单簿中,并获得约 4.3% 的利息收益。这些收益每年可为 Circle Internet Financial 带来约 1.075 亿美元的收入,流入其私人资产负债表。每一笔新存入 Hyperliquid 的 USDC,都在进一步扩大 Circle 的现金流。但如果这些价值不是流向 Circle,而是反过来用于壮大 Hyperliquid 生态,会怎么样?在有机会突破现有框架的情况下,我们为什么还要被 USDC 这种过时的传统稳定币模式所束缚?
选择沿用旧稳定币的机会成本
随着 Hyperliquid 在链上交易中的影响力不断扩大,法币稳定币的净存款也随之增长,为永续合约市场和现货市场提供流动性。在一个 Hyperliquid 增长 10 倍、100 倍、甚至 1000 倍的未来里,继续使用传统稳定币的机会成本也会越来越高。这些来自稳定币层的价值,要么继续流向 Circle 和 Tether 的资产负债表,要么回流到 Hyperliquid 自身生态中。
为 Hyperliquid 量身打造的新稳定币模型
「援助基金」(Assistance Fund)通过自动回购 HYPE 已经证明:协议产生的现金流完全可以、也应该直接回馈给社区。仅过去 30 天,援助基金就从市场中回收了数百万美元的 HYPE。
HUSD 延续这一策略,只不过它是在稳定币层面展开:一开始,HUSD 所带来的利息收入中,一大部分将用于购买 HYPE,然后把这些 HYPE 再部署到 Hyperliquid 生态的各个增长方向上。换句话说,每一次你使用 HUSD,都会为 HYPE 增加买压,并把价值重新投入 Hyperliquid 的发展中。
被回购的 HYPE 将如何被使用?
HUSD:为 Builder Code 未来提供燃料
HUSD 在推动「Builder Code」商业模式的爆发中起着关键作用。Builder Code 是 Hyperliquid 的原生功能,允许一个界面运营者(interface operator)在代表用户提交的现货或合约交易中收取一定费用。它的目标是为 Hyperliquid 的「最后一公里分发」提供变现方式——也就是说,任何能有效吸引并留住用户的人,都可以通过 Builder Code 建立起一个不受技术或流动性限制的交易业务。
这类业务的单位经济效益可能非常可观,但在目前这个早期阶段,新品牌仍面临「冷启动」问题,而不同接口之间的护城河也还不明显。HUSD 的出现,可以帮助这些「Hyperliquid 混合体」完成启动,同时提供一种方法让它们之间形成差异化。
通过 HUSD 补贴 Builder Code 的费用,接口可以向用户收取比原本更高的费用,却不增加用户成本。接口能实时获得收入,并进一步将这些资金用于增长策略。
举个例子:假设 Interface XYZ 获得了 100 HUSD 的返利预算。所有带有其 Builder Code 的合约交易都会被系统统计,相应用户的返利余额也会不断增长。在用户真正开始承担费用之前,该接口至少可以处理约 $100,000 的合约交易量(即 100 HUSD 除以 0.1% 的手续费率)。与此同时,接口运营者也可以把 Builder Code 带来的收入再投入到拉新或用户留存中。
这就是 HUSD 为 Hyperliquid 生态「实时增长」提供动力的方式。
总结
HUSD 融合了两个核心洞察:将交易使用的计价资产(稳定币)以及由它产生的现金流,统一纳入交易平台体系内。最终结果,就是一个「公共产品」性质的稳定币,它将原本静态的储备利息,转化为 Hyperliquid 生态的主动式、复利式增长。
HUSD 是一个由 Felix 运营、社区成员支持的公共产品项目,它将通过 Felix Points 系统上线。这一部署也建立在 @m0foundation 打下的基础之上,正是其对「全球稳定币平台」的愿景,才让 HUSD 成为可能。
Hyperliquid 已经颠覆了中心化交易所的格局,而 HUSD 正准备对传统法币稳定币做同样的事。
「原文链接」
1.47万
0
GMX 价格表现 (美元)
GMX 当前价格为 $15.1800。GMX 的价格在过去 24 小时内上涨了 +2.22%。目前,GMX 市值排名为第 153 名,实时市值为 $1.54亿,流通供应量为 10,136,797 GMX,最大供应量为 13,250,000 GMX。我们会实时更新 GMX/USD 的价格。
今日
+$0.33000
+2.22%
7 天
-$0.59000
-3.75%
30 天
-$0.16000
-1.05%
3 个月
-$4.5000
-22.87%
关于 GMX (GMX)
此评级是欧易从不同来源收集的汇总评级,仅供一般参考。欧易不保证评级的质量或准确性。欧易无意提供 (i) 投资建议或推荐;(ii) 购买、出售或持有数字资产的要约或招揽;(iii) 财务、会计、法律或税务建议。包括稳定币和 NFT 的数字资产容易受到市场波动的影响,风险较高,波动较大,可能会贬值甚至变得一文不值。数字资产的价格和性能不受保证,且可能会发生变化,恕不另行通知。您的数字资产不受潜在损失保险的保障。 历史回报并不代表未来回报。欧易不保证任何回报、本金或利息的偿还。欧易不提供投资或资产建议。您应该根据自身的财务状况仔细考虑交易或持有数字资产是否适合您。具体情况请咨询您的专业法务、税务或投资人士。
展开更多
- 官网
- Github
- 区块浏览器
关于第三方网站
关于第三方网站
通过使用第三方网站(“第三方网站”),您同意对第三方网站的任何使用均受第三方网站条款的约束和管辖。除非书面明确说明,否则 OKX 及其关联方(“OKX”)与第三方网站的所有者或运营商没有任何关联。您同意 OKX 对您使用第三方网站而产生的任何损失、损害和任何其他后果不承担任何责任。请注意,使用第三方网站可能会导致您的资产损失或贬值。
GMX 常见问题
GMX 今天值多少钱?
目前,一个 GMX 价值是 $15.1800。如果您想要了解 GMX 价格走势与行情洞察,那么这里就是您的最佳选择。在欧易探索最新的 GMX 图表,进行专业交易。
数字货币是什么?
数字货币,例如 GMX 是在称为区块链的公共分类账上运行的数字资产。了解有关欧易上提供的数字货币和代币及其不同属性的更多信息,其中包括实时价格和实时图表。
数字货币是什么时候开始的?
由于 2008 年金融危机,人们对去中心化金融的兴趣激增。比特币作为去中心化网络上的安全数字资产提供了一种新颖的解决方案。从那时起,许多其他代币 (例如 GMX) 也诞生了。
GMX 的价格今天会涨吗?
查看 GMX 价格预测页面,预测未来价格,帮助您设定价格目标。
ESG 披露
ESG (环境、社会和治理) 法规针对数字资产,旨在应对其环境影响 (如高能耗挖矿)、提升透明度,并确保合规的治理实践。使数字代币行业与更广泛的可持续发展和社会目标保持一致。这些法规鼓励遵循相关标准,以降低风险并提高数字资产的可信度。
资产详情
名称
OKcoin Europe LTD
相关法人机构识别编码
54930069NLWEIGLHXU42
代币名称
GMX
共识机制
GMX is present on the following networks: arbitrum, avalanche.
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 solution on top of Ethereum that uses Optimistic Rollups to enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs. It assumes that transactions are valid by default and only verifies them if there's a challenge (optimistic): Core Components: • Sequencer: Orders transactions and creates batches for processing. • Bridge: Facilitates asset transfers between Arbitrum and Ethereum. • Fraud Proofs: Protect against invalid transactions through an interactive verification process. Verification Process: 1. Transaction Submission: Users submit transactions to the Arbitrum Sequencer, which orders and batches them. 2. State Commitment: These batches are submitted to Ethereum with a state commitment. 3. Challenge Period: Validators have a specific period to challenge the state if they suspect fraud. 4. Dispute Resolution: If a challenge occurs, the dispute is resolved through an iterative process to identify the fraudulent transaction. The final operation is executed on Ethereum to determine the correct state. 5. Rollback and Penalties: If fraud is proven, the state is rolled back, and the dishonest party is penalized. Security and Efficiency: The combination of the Sequencer, bridge, and interactive fraud proofs ensures that the system remains secure and efficient. By minimizing on-chain data and leveraging off-chain computations, Arbitrum can provide high throughput and low fees.
The Avalanche blockchain network employs a unique Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism called Avalanche Consensus, which involves three interconnected protocols: Snowball, Snowflake, and Avalanche. Avalanche Consensus Process 1. Snowball Protocol: o Random Sampling: Each validator randomly samples a small, constant-sized subset of other validators. Repeated Polling: Validators repeatedly poll the sampled validators to determine the preferred transaction. Confidence Counters: Validators maintain confidence counters for each transaction, incrementing them each time a sampled validator supports their preferred transaction. Decision Threshold: Once the confidence counter exceeds a pre-defined threshold, the transaction is considered accepted. 2. Snowflake Protocol: Binary Decision: Enhances the Snowball protocol by incorporating a binary decision process. Validators decide between two conflicting transactions. Binary Confidence: Confidence counters are used to track the preferred binary decision. Finality: When a binary decision reaches a certain confidence level, it becomes final. 3. Avalanche Protocol: DAG Structure: Uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure to organize transactions, allowing for parallel processing and higher throughput. Transaction Ordering: Transactions are added to the DAG based on their dependencies, ensuring a consistent order. Consensus on DAG: While most Proof-of-Stake Protocols use a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus, Avalanche uses the Avalanche Consensus, Validators reach consensus on the structure and contents of the DAG through repeated Snowball and Snowflake.
奖励机制与相应费用
GMX is present on the following networks: arbitrum, avalanche.
Arbitrum One, a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, employs several incentive mechanisms to ensure the security and integrity of transactions on its network. The key mechanisms include: 1. Validators and Sequencers: o Sequencers are responsible for ordering transactions and creating batches that are processed off-chain. They play a critical role in maintaining the efficiency and throughput of the network. o Validators monitor the sequencers' actions and ensure that transactions are processed correctly. Validators verify the state transitions and ensure that no invalid transactions are included in the batches. 2. Fraud Proofs: o Assumption of Validity: Transactions processed off-chain are assumed to be valid. This allows for quick transaction finality and high throughput. o Challenge Period: There is a predefined period during which anyone can challenge the validity of a transaction by submitting a fraud proof. This mechanism acts as a deterrent against malicious behavior. o Dispute Resolution: If a challenge is raised, an interactive verification process is initiated to pinpoint the exact step where fraud occurred. If the challenge is valid, the fraudulent transaction is reverted, and the dishonest actor is penalized. 3. Economic Incentives: o Rewards for Honest Behavior: Participants in the network, such as validators and sequencers, are incentivized through rewards for performing their duties honestly and efficiently. These rewards come from transaction fees and potentially other protocol incentives. o Penalties for Malicious Behavior: Participants who engage in dishonest behavior or submit invalid transactions are penalized. This can include slashing of staked tokens or other forms of economic penalties, which serve to discourage malicious actions. Fees on the Arbitrum One Blockchain 1. Transaction Fees: o Layer 2 Fees: Users pay fees for transactions processed on the Layer 2 network. These fees are typically lower than Ethereum mainnet fees due to the reduced computational load on the main chain. o Arbitrum Transaction Fee: A fee is charged for each transaction processed by the sequencer. This fee covers the cost of processing the transaction and ensuring its inclusion in a batch. 2. L1 Data Fees: o Posting Batches to Ethereum: Periodically, the state updates from the Layer 2 transactions are posted to the Ethereum mainnet as calldata. This involves a fee, known as the L1 data fee, which accounts for the gas required to publish these state updates on Ethereum. o Cost Sharing: Because transactions are batched, the fixed costs of posting state updates to Ethereum are spread across multiple transactions, making it more cost-effective for users.
Avalanche uses a consensus mechanism known as Avalanche Consensus, which relies on a combination of validators, staking, and a novel approach to consensus to ensure the network's security and integrity. Validators: Staking: Validators on the Avalanche network are required to stake AVAX tokens. The amount staked influences their probability of being selected to propose or validate new blocks. Rewards: Validators earn rewards for their participation in the consensus process. These rewards are proportional to the amount of AVAX staked and their uptime and performance in validating transactions. Delegation: Validators can also accept delegations from other token holders. Delegators share in the rewards based on the amount they delegate, which incentivizes smaller holders to participate indirectly in securing the network. 2. Economic Incentives: Block Rewards: Validators receive block rewards for proposing and validating blocks. These rewards are distributed from the network’s inflationary issuance of AVAX tokens. Transaction Fees: Validators also earn a portion of the transaction fees paid by users. This includes fees for simple transactions, smart contract interactions, and the creation of new assets on the network. 3. Penalties: Slashing: Unlike some other PoS systems, Avalanche does not employ slashing (i.e., the confiscation of staked tokens) as a penalty for misbehavior. Instead, the network relies on the financial disincentive of lost future rewards for validators who are not consistently online or act maliciously. o Uptime Requirements: Validators must maintain a high level of uptime and correctly validate transactions to continue earning rewards. Poor performance or malicious actions result in missed rewards, providing a strong economic incentive to act honestly. Fees on the Avalanche Blockchain 1. Transaction Fees: Dynamic Fees: Transaction fees on Avalanche are dynamic, varying based on network demand and the complexity of the transactions. This ensures that fees remain fair and proportional to the network's usage. Fee Burning: A portion of the transaction fees is burned, permanently removing them from circulation. This deflationary mechanism helps to balance the inflation from block rewards and incentivizes token holders by potentially increasing the value of AVAX over time. 2. Smart Contract Fees: Execution Costs: Fees for deploying and interacting with smart contracts are determined by the computational resources required. These fees ensure that the network remains efficient and that resources are used responsibly. 3. Asset Creation Fees: New Asset Creation: There are fees associated with creating new assets (tokens) on the Avalanche network. These fees help to prevent spam and ensure that only serious projects use the network's resources.
信息披露时间段的开始日期
2024-04-20
信息披露时间段的结束日期
2025-04-20
能源报告
能源消耗
2660.23259 (kWh/a)
能源消耗来源与评估体系
The energy consumption of this asset is aggregated across multiple components:
To determine the energy consumption of a token, the energy consumption of the network(s) arbitrum, avalanche is calculated first. Based on the crypto asset's gas consumption per network, the share of the total consumption of the respective network that is assigned to this asset is defined. When calculating the energy consumption, we used - if available - the Functionally Fungible Group Digital Token Identifier (FFG DTI) to determine all implementations of the asset of question in scope and we update the mappings regulary, based on data of the Digital Token Identifier Foundation.




















社媒平台热度