
FXS
Frax Share Kurs
$3,7960
-$0,03500
(-0,92 %)
Preisänderung der letzten 24 Stunden

Was denken Sie heute über den FXS-Kurs?
Teilen Sie uns Ihre Meinung mit: Daumen nach oben, wenn Sie BTC und seinen Wert positiv sehen, oder Daumen nach unten, wenn Sie ihn negativ einschätzen.
Abstimmen und Ergebnisse anzeigen
Haftungsausschluss
Der soziale Inhalt auf dieser Seite („Inhalt”), einschließlich, aber nicht beschränkt auf Tweets und Statistiken, die von LunarCrush bereitgestellt werden, stammt von Dritten und wird „wie er ist” ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bereitgestellt. OKX übernimmt keine Garantie für die Qualität oder Richtigkeit des Inhalts, und der Inhalt spiegelt nicht die Ansichten von OKX wider. Die Inhalte dienen nicht dazu, (i) Anlageberatung oder Empfehlungen zu geben, (ii) ein Angebot oder eine Aufforderung zum Kauf, Verkauf oder Halten digitaler Vermögenswerte darzustellen oder (iii) finanzielle, buchhalterische, rechtliche oder steuerliche Beratung zu leisten. Digitale Assets, einschließlich Stablecoins und NFTs, bergen ein hohes Risiko, können stark schwanken und sogar wertlos werden. Preis und Leistung digitaler Vermögenswerte sind nicht garantiert und können sich ohne Vorankündigung ändern.<br></br>OKX gibt keine Anlage- oder Vermögensempfehlungen. Du solltest gut abwägen, ob der Handel und das Halten von digitalen Assets angesichts deiner finanziellen Situation sinnvoll ist. Bei Fragen zu deiner individuellen Situation wende dich bitte an deinen Rechts-/Steuer- oder Anlagenexperten. Weitere Einzelheiten findest du in unseren <a href="/help/terms-of-service">Nutzungsbedingungen</a> und der <a href="/help/risk-compliance-disclosure">Risikowarnung</a>. Durch die Nutzung der Website eines Drittanbieters („TPW“) akzeptieren Sie, dass jegliche Nutzung der TPW den Bedingungen der TPW unterliegt. Sofern nicht ausdrücklich schriftlich angegeben, steht OKX einschließlich seiner verbundenen Unternehmen („OKX“) in keinerlei Verbindung zum Eigentümer oder Betreiber der TPW. Sie stimmen zu, dass OKX nicht für Verluste, Schäden oder sonstige Folgen haftet, die sich aus Ihrer Nutzung der TPW ergeben. Bitte beachte, dass die Nutzung einer TPW zu einem Verlust oder einer Minderung deiner Assets führen kann. Das Produkt ist möglicherweise nicht in allen Ländern verfügbar.
Marktinformationen zu Frax Share
Marktkapitalisierung
Die Marktkapitalisierung wird durch Multiplikation der Umlaufmenge des Coins mit dem letzten Preis berechnet.
Marktkapitalisierung = Umlaufmenge × letzter Preis
Marktkapitalisierung = Umlaufmenge × letzter Preis
Umlaufmenge
Gesamtmenge eines Coins, die auf dem Markt öffentlich verfügbar ist.
Ranking der Marktkapitalisierung
Platzierung des Coins in Bezug auf die Marktkapitalisierung.
Allzeithoch
Höchster Preis, den ein Coin in seiner Handelsgeschichte erreicht hat.
Allzeittief
Niedrigster Preis, den ein Coin in seiner Handelshistorie erreicht hat.
Marktkapitalisierung
$344,50M
Umlaufmenge
90.657.201 FXS
90,94 % von
99.681.496 FXS
Ranking der Marktkapitalisierung
103
Prüfungen

Letzte Prüfung: 23. Mai 2021
24-Std.-Hoch
$3,9600
24-Std.-Tief
$3,6070
Allzeithoch
$11,0000
-65,50 % (-$7,2040)
Letzte Aktualisierung: 6. Juli 2023
Allzeittief
$1,2460
+204,65 % (+$2,5500)
Letzte Aktualisierung: 11. März 2025
Frax Share-Feed
Der folgende Inhalt stammt von .

Phan Đạt
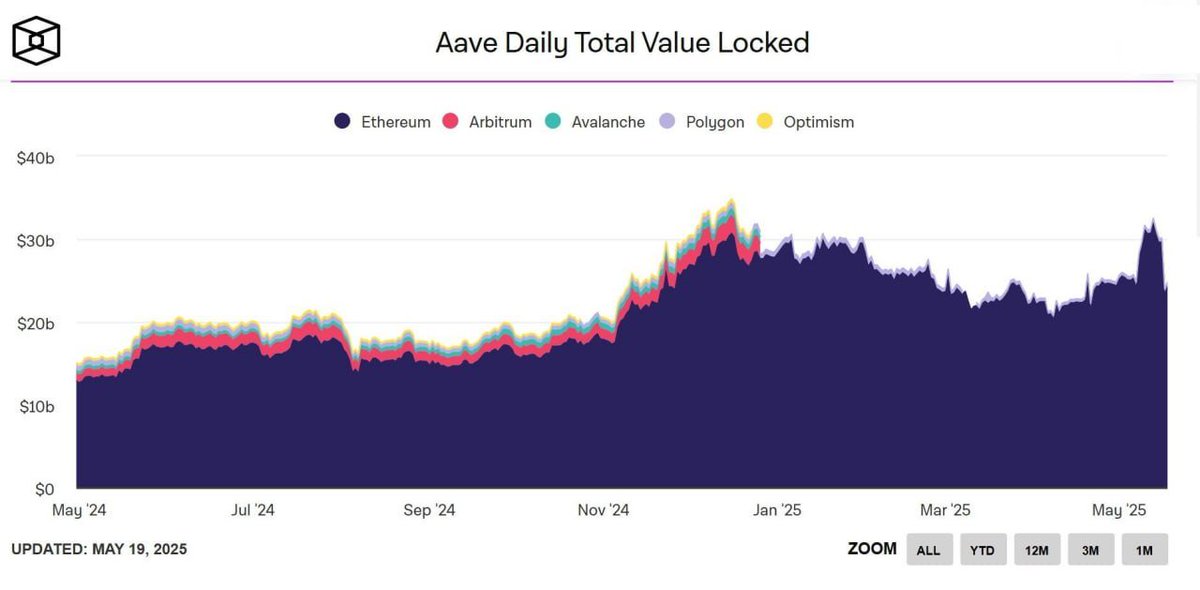
Der TVL von $AAVE ist deutlich gestiegen; Könnte der DeFi Summer ein Comeback feiern?
Der Total Value Locked (TVL) von $AAVE hat $LIDO übertroffen und ist vom Jahrestief von 20 Milliarden US-Dollar um 50 % auf ein Allzeithoch am 12. Mai mit 40 Milliarden US-Dollar gestiegen, was seine Position als führendes Kreditprotokoll auf Ethereum und als zweitgrößte dezentrale Anwendung nach TVL festigt.
Diese Erholung ist ein starkes Vertrauen in das DeFi-Ökosystem von Ethereum, das Anfang des Jahres einen Rückgang der Aktivität verzeichnet hatte. Zum Zeitpunkt der Erstellung dieses Artikels generiert $AAVE über 1 Million US-Dollar an täglichen Transaktionsgebühren, was darauf hindeutet, dass die aktive Protokollnutzung weit über passive Kapitaleinlagen hinausgeht.
$AAVE beweist seine Überlegenheit sowohl bei der Produkt- als auch bei der Token-Preisentwicklung trotz der Trägheit von Ethereum und der "Aggressivität" des Solana-Ökosystems.
Derzeit schwankt $AAVE bei einem Preis von 260 $, was das Wachstum einer Reihe anderer DeFi-Protokolle vorantreibt.
Wenn der DeFi-Sommer wirklich stattfindet, sind dies die DeFi-Projekte, die jeder im Auge behalten sollte:
$COW (CoW Protocol): Ein DeFi-Protokoll, das sich auf die Optimierung von Transaktionen durch den "Coincidence of Wants"-Mechanismus, die Reduzierung der Gaskosten und die Vermeidung von Front-Running konzentriert. Es bietet eine dezentrale Austauschlösung mit einer reibungslosen Benutzererfahrung, die in DEX-Plattformen integriert ist.
$ENA (Ethena): Ein Projekt, das den dezentralen Stablecoin USDe entwickelt, der durch Ethereum-Staking-Assets unterstützt wird und eine delta-neutrale Strategie verwendet, um stabile Preise zu erhalten. Ethena zielt darauf ab, eine hochverzinsliche, risikoarme dezentrale Finanzlösung anzubieten.
$FXS (Frax Share): Der Governance-Token des Frax Protocol, ein hybrides Stablecoin-System (teilweise besichert) mit FRAX als Haupt-Stablecoin. FXS wird für Abstimmungen, Staking und Gewinnbeteiligung verwendet und unterstützt die FRAX-Preisstabilität durch einen algorithmischen Mechanismus.
$PENDLE: Ein DeFi-Protokoll, das die Tokenisierung und den Handel mit zukünftigen Erträgen ermöglicht. Pendle trennt die Rendite vom Staking von Vermögenswerten oder der Liquiditätsbereitstellung und schafft so einen Markt für den Kauf, Verkauf oder die Absicherung von Renditen.
#DeFi
Original anzeigen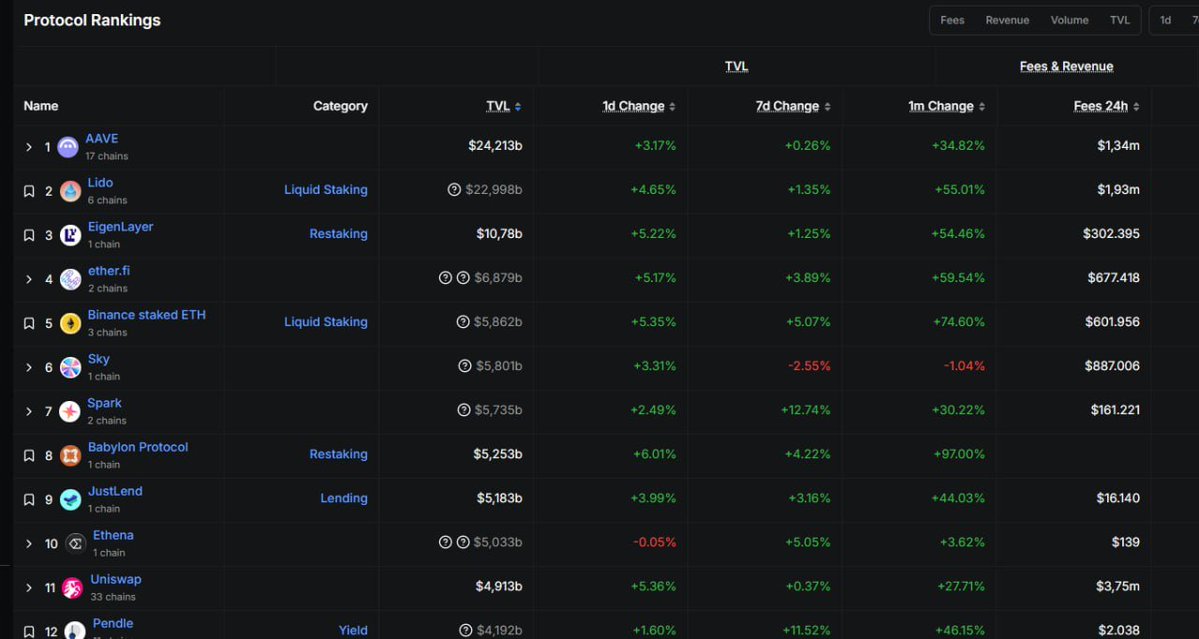
29.041
9

TechFlow
Von Alex Liu, Foresight News
Der Stablecoin Act vs. FXS
Am 20. Mai wurde der GENIUS Act, ein Gesetzentwurf für Stablecoins in den Vereinigten Staaten, im Senat verabschiedet, und es sind noch zwei wichtige Schritte bis zur Abstimmung im Repräsentantenhaus und der Unterschrift des Präsidenten. Die Märkte glaubten zuvor, dass eine Abstimmung im Senat das größte Hindernis für die Verabschiedung des Gesetzes sei, und wenn es keine Überraschungen gebe, sei es nur eine Frage der Zeit, bis das Gesetz vollständig verabschiedet werde.
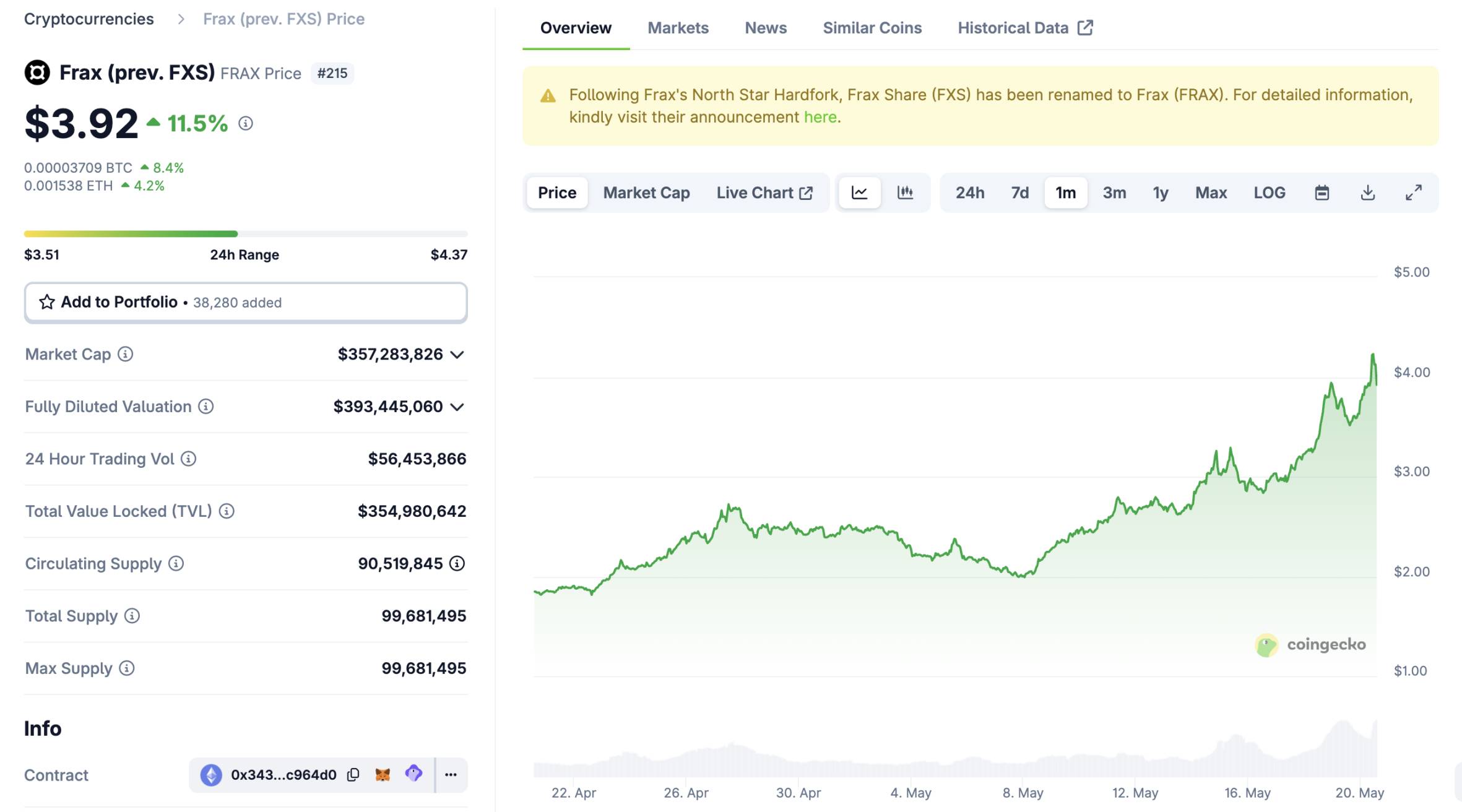
Welches Krypto-Projekt ist der größte Gewinner dieses legislativen Sieges? In Bezug auf die Wertentwicklung des Token-Preises könnte es Frax Finance sein.
Mit der Verabschiedung des Gesetzentwurfs im Senat stieg der Frax Finance-Token FXS (jetzt in FRAX umbenannt, der an den zentralisierten Börsen noch nicht aktualisiert wurde) kurzzeitig über 4,4 USDT und belegte damit den ersten Platz unter den Mainstream-Börsen. Selbst mit einer leichten Korrektur des Preises im Moment sind die FXS im Laufe des Monats immer noch um mehr als 100% gestiegen.
Warum ist das Gesetz gut für Frax Finance und warum wird Frax von einigen als der größte Gewinner des GENIUS Act angesehen?
Frax Finanzen
Bei den Produkten von Frax Finance handelt es sich nicht nur um Stablecoins, sondern auch um Liquid Staking, Lending, L2 und mehr. Aber sie haben tiefe Wurzeln in den Stablecoins. Frax war früher der Emittent des hybriden algorithmischen Stablecoins FRAX, gab aber nach dem Crash von Luna UST den "rechnerischen" Weg auf und wandelte sich in einen vollständig besicherten Stablecoin um.
Seitdem wurde FRAX weiter auf frxUSD aktualisiert, das durch Fiat-Währung gesichert ist, "mit der gesamten Roadmap, der erste lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin zu werden".
Frax-Gründer Sam deutete an, dass Frax am meisten von dem Gesetz profitiert habe
Aber warum wurde frxUSD der "erste" lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin vor USDC, USDY und anderen Produkten? Auf regulatorischer Ebene hat es wirklich die Möglichkeit, "nah am Wasser zu sein und zuerst den ersten Monat zu bekommen".
Sam Kazemian, der Gründer von Frax Finance, hat seit Anfang des Jahres häufig Fotos von sich mit Krypto-Gesetzgebern in Washington, D.C., gepostet. Es wird gemunkelt, dass er als Brancheninsider stark in die Diskussion und Ausarbeitung des GENIUS Act involviert war. Der Markt scheint den regulatorischen Vorteil, den Frax Finance entsprechend haben wird, einzupreisen.
Sam posiert mit kryptofreundlichem Senator Lummis
Wenn die Spekulationen wahr sind, hat Sam als Verfasser und Teilnehmer des Gesetzentwurfs natürlich ein tieferes Verständnis für den GENIUS Act, und es ist für sein Projekt einfacher, die Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Darüber hinaus bleibt abzuwarten, ob die freundschaftlichen Beziehungen zum Gesetzgeber regulatorisch grünes Licht für die Zukunft von FRAX geben werden.
Der zukünftige Weg von FRAX
Zusätzlich zu den potenziellen regulatorischen Möglichkeiten baut FRAX ein vertikal integriertes Stablecoin-Ökosystem auf, das frxUSD (Stablecoin), FraxNet (Bankschnittstelle) und Fraxtal (L2 Execution Layer) umfasst, um den Anforderungen des zukünftigen regulatorischen Umfelds gerecht zu werden:
frxUSD: Als Stablecoin für FRAX, 1:1 an den US-Dollar gekoppelt.
FraxNet: Eine Banking-Schnittstelle, die entwickelt wurde, um das traditionelle Finanzsystem mit DeFi zu verbinden.
Fraxtal: Eine L2-Ausführungsschicht (oder eine allmähliche Umstellung auf L1), die effizienten Handel und Skalierbarkeit bietet.
Die Token-Restrukturierung ist auch Teil der Zukunftspläne von FRAX. FXS wurde in FRAX umbenannt und mit Funktionen wie Gas, Governance, Burning und Staking ausgestattet. Diese Änderung zielt darauf ab, die Funktionalität und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit von FRAX zu verbessern und es dem Unternehmen zu ermöglichen, flexibler in einer konformen Umgebung zu arbeiten.
Wenn Sie FRAX als veFRAX einsetzen, können Sie potenzielle Belohnungen wie FXTL (Frax' eigene Punkte), Karak, Ethena und Symbiotic-Punkte erhalten.
Die Gründer betreiben aktiv und beteiligen sich an der Gesetzgebung im Zusammenhang mit Stablecoins, und ihre eigene Produkt-Roadmap wird aktiv an narrative Dienstleistungen angepasst. Mit der weiteren Umsetzung des GENIUS Act ist die Performance von FXS (FRAX) es wert, dass man sich darauf freut.
Original anzeigen

8.163
0

比特币橙子Trader
Orange Abenddolmetschung 17.20 Uhr
Der GENIUS Stablecoin Gesetzentwurf geht im Senat noch einen Schritt weiter! Der Kryptomarkt kocht, der #RWA #Stablecoin Sektor hebt ab, das Kapitalengagement könnte 2 Billionen erreichen, die US-Dollar-Hegemonie + das neue Spiel der US-Anleihen, und der Nachahmerbulle ist zu erwarten?
Die größte Neuigkeit gestern Abend war, dass der GENIUS-Stablecoin-Gesetzentwurf die zweite Abstimmung über den Verfahrensantrag im Senat passiert hat, obwohl dies nicht bedeutet, dass der Gesetzentwurf verabschiedet wurde, aber im Vergleich zu den negativen am 8. Mai aufgrund des Rückzugs der Unterstützung durch die Demokratische Partei (Bedenken hinsichtlich der Bekämpfung von Geldwäsche und Trumps Interessenkonflikt) die Verfahrensabstimmung nicht bestanden hat, was auch dem zweiten Neustart des Gesetzentwurfs entspricht, besteht das nächste Verfahren darin, dass der Senat debattiert und Änderungen vornimmt, der Senat stimmt schließlich ab, das Repräsentantenhaus dekretiert, die beiden Häuser koordinieren sich und der Präsident unterzeichnet, obwohl es noch ein langer Weg ist, bis der Gesetzentwurf endgültig verabschiedet wird Letzte Nacht hat sogar der Krypto-Zar David Sacks ein Dokument veröffentlicht, in dem es heißt, dass die Verabschiedung des Antrags ein großer Sieg im Bereich der Kryptowährungen ist, der CEO von Coinbase glaubt auch, dass die Verabschiedung des Gesetzes ein großer Sieg für die On-Chain-Innovation sein wird, und der Berater für digitale Vermögenswerte des Weißen Hauses, Bo Hines, glaubt, dass es bei dem Genius-Gesetz darum geht, die Dominanz des US-Dollars zu konsolidieren und die weltweit führende US-Asset-Innovation ist.
Viele kleine Partner sind möglicherweise nicht in der Lage, herauszufinden, was die spezifischen Vorteile dieses Gesetzentwurfs für Krypto sind, erstens bringt er ein enormes Kapitalrisiko mit sich, die Stablecoins USDC und USDT, die wir jetzt verwenden, sind in den Augen der Wall Street immer noch Nischenanlagen, und die Beschränkung großer Fonds auf dem Markt ist eigentlich Compliance und Regulierung, wenn die Stablecoin-Antwort verabschiedet wird, dann werden die Institutionen keine Sorgen haben, Elizabeth Warren schätzte sogar, dass dieser Gesetzentwurf zu einem Anstieg des Stablecoin-Marktes von 200 Milliarden auf 2W US-Dollar führen wird, was dem kanadischen BIP entspricht. Sie sagen, dass diese Größenordnung an Geldern in den Devisenmarkt eingedrungen ist, ist es so, dass die Hühner und Hunde in den Himmel aufgestiegen sind und das Bauernvieh sich immer noch Sorgen machen muss?
Der zweite ist, dass der globale Status des US-Dollars garantiert wurde und der On-Chain-Stablecoin und die On-Chain-Investitionen zu einem neuen Reservoir für US-Anleihen geworden sind, unabhängig davon, ob der neue Stablecoin 1 USD oder 2 USD beträgt, und der letzte Anker sind US-Anleihen. Die Nachrichten von gestern Abend haben die deutschen Reserven überschritten, wenn in Zukunft Dutzende oder Hunderte von Fesseln geschaffen werden, fürchte ich, dass die US-Schulden nicht ausreichen, damit die US-Schuldenkrise unter Kontrolle gebracht wird, es ist möglich, dass Trump vor seinem Amtsantritt gesagt hat, dass er sich auf Verschlüsselung verlassen will, um das US-Schuldenproblem zu lösen, und sich letztendlich auf den Stablecoin-Plan verlassen will, wenn dies der Fall ist, dann wird bei der aktuellen US-Schuldenskala von 3,7 Milliarden die Menge an Geldern, die in die Kette und den Devisenmarkt gebracht werden, größer sein, also wenn dieses Gesetz verabschiedet wird, Es ist definitiv ein super positiver Wert, der das Niveau des Bitcoin-Spot-ETFs oder der nationalen strategischen Reserven übertrifft.
Genau wegen dieses Gesetzentwurfs hat der heutige #rwa #stablecoin Sektor Fahrt aufgenommen, lassen Sie uns zuerst über RWA sprechen, denn Stablecoins sind gleichwertige Vermögenswerte, die an US-Anleihen oder den US-Dollar gebunden sind, also sind sie eigentlich reale Vermögenswerte, das heißt, RWA, und da der US-Dollar in der Kette sein kann, können auch andere physische Vermögenswerte und Finanzanlagen in der Kette sein, und der Weg in die Kette sollte die bestehende Infrastruktur sein, also ist #rwa definitiv eine Superplatte für eine lange Zeit in der Zukunft. Heute sind im Grunde alle RWA-bezogenen Projekte in Schwung gekommen, insbesondere mehrere RWA-Emporkömmlinge in der Kette, $collat $kta $token $mpl und so weiter, sind um mehr als 30 % gestiegen, und mehrere führende Trends sind auch sehr stark$ondo $link $mkr $syrup $om usw., mit einem Anstieg von mehr als 5 % an einem Tag;
Dann gibt es noch das Stablecoin-Protokoll, obwohl heute viel darüber gesprochen wird, dass die Stablecoin-Rechnung tatsächlich negativ für das bestehende dezentrale Stablecoin-Protokoll ist, denn in Zukunft wird der Markt den US-Dollar nur noch als Sicherheiten-Stablecoin erkennen, und das bestehende Stablecoin-Protokoll soll sich seit seiner Geburt mit zentralisierter Fiat-Währung befassen, entwarf eine Vielzahl von Mechanismen in der Hoffnung, die Fiat-Währung zu optimieren, so dass das Gewitter von Luna im Grunde jeden die Obergrenze der reinen Algorithmus-Stablecoins sehen ließ, die überbesicherten oder semi-algorithmischen sind entweder ineffizient oder leicht zu entankern In der Tat ist es schwierig, eine zu große Platte zu unterstützen, theoretisch wird es in Zukunft Hunderte von USDT geben, und es gibt in der Tat keinen Platz für stabile und dezentrale Stablecoins, aber kurzfristig gibt es immer noch Spekulationen, und der $aave $fxs $ena $pendle $crv der letzten Nacht war im Grunde ein Anstieg von etwa 10-20%, was darauf hindeutet, dass CEX keine andere Wahl hat, als dieses Konzept zu spielen;
Wenn Sie den Hund an der Kette hetzen, gibt es letzte Nacht wirklich nichts zu spielen, ich habe in meinem vorherigen Artikel erwähnt, dass das Spiel des Glaubens zu viel Vor-Ort-Geld an das traditionelle Web2 gegeben hat, was dazu geführt hat, dass das Vertrauen und die Emotionen von Lauch stark gesunken sind, also ist es ein kurzfristiges Ende, und der nächste Markt muss möglicherweise zum Mainstream-Narrativ zurückkehren, RWA, AI, DeFi, Payfi, L1, aber die echte Hüttenkuh muss auf das offizielle ATH des Kuchens warten, diese Runde von Hüttenrindern kann nach dem Kuchen 12W stattfinden, alle seien Sie geduldig und warten Sie.
Original anzeigen
74.796
11

Blockbeats
Originaltitel: "Warum wurde FRAX nach der Verabschiedung des Stablecoin-Gesetzes zum größten Gewinner?" 》
Originalartikel von Alex Liu, Foresight News
Der Stablecoin Act vs. FXS
Am 20. Mai wurde der GENIUS Act, ein Gesetzentwurf für Stablecoins in den Vereinigten Staaten, im Senat verabschiedet, und es sind noch zwei wichtige Schritte bis zur Abstimmung im Repräsentantenhaus und der Unterschrift des Präsidenten. Die Märkte glaubten zuvor, dass eine Abstimmung im Senat das größte Hindernis für die Verabschiedung des Gesetzes sei, und wenn es keine Überraschungen gebe, sei es nur eine Frage der Zeit, bis das Gesetz vollständig verabschiedet werde.
Welches Krypto-Projekt ist der größte Gewinner dieses legislativen Sieges? In Bezug auf die Wertentwicklung des Token-Preises könnte es Frax Finance sein.
Mit der Verabschiedung des Gesetzentwurfs im Senat stieg der Frax Finance-Token FXS (jetzt in FRAX umbenannt, der an den zentralisierten Börsen noch nicht aktualisiert wurde) kurzzeitig über 4,4 USDT und belegte damit den ersten Platz unter den Mainstream-Börsen. Selbst mit einer leichten Korrektur des Preises im Moment sind die FXS im Laufe des Monats immer noch um mehr als 100% gestiegen.
Warum ist das Gesetz gut für Frax Finance und warum wird Frax von einigen als der größte Gewinner des GENIUS Act angesehen?
Frax Finanzen
Bei den Produkten von Frax Finance handelt es sich nicht nur um Stablecoins, sondern auch um Liquid Staking, Lending, L2 und mehr. Aber sie haben tiefe Wurzeln in den Stablecoins. Frax war früher der Emittent des hybriden algorithmischen Stablecoins FRAX, gab aber nach dem Crash von Luna UST den "rechnerischen" Weg auf und wandelte sich in einen vollständig besicherten Stablecoin um.
Seitdem wurde FRAX weiter auf frxUSD aktualisiert, das durch Fiat-Währung gesichert ist, "mit der gesamten Roadmap, der erste lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin zu werden".
Frax-Gründer Sam deutete an, dass Frax am meisten von dem Gesetz profitiert habe
Aber warum wurde frxUSD der "erste" lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin vor USDC, USDY und anderen Produkten? Auf regulatorischer Ebene hat es wirklich die Möglichkeit, "nah am Wasser zu sein und zuerst den ersten Monat zu bekommen".
Sam Kazemian, der Gründer von Frax Finance, hat seit Anfang des Jahres häufig Fotos von sich mit Krypto-Gesetzgebern in Washington, D.C., gepostet. Es wird gemunkelt, dass er als Brancheninsider stark in die Diskussion und Ausarbeitung des GENIUS Act involviert war. Der Markt scheint den regulatorischen Vorteil, den Frax Finance entsprechend haben wird, einzupreisen.
Sam posiert mit kryptofreundlichem Senator Lummis
Wenn die Spekulationen wahr sind, hat Sam als Verfasser und Teilnehmer des Gesetzentwurfs natürlich ein tieferes Verständnis für den GENIUS Act, und es ist für sein Projekt einfacher, die Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Darüber hinaus bleibt abzuwarten, ob die freundschaftlichen Beziehungen zum Gesetzgeber regulatorisch grünes Licht für die Zukunft von FRAX geben werden.
Der zukünftige Weg von FRAX
Zusätzlich zu den potenziellen regulatorischen Möglichkeiten baut FRAX ein vertikal integriertes Stablecoin-Ökosystem auf, das frxUSD (Stablecoin), FraxNet (Bankschnittstelle) und Fraxtal (L2 Execution Layer) umfasst, um den Anforderungen des zukünftigen regulatorischen Umfelds gerecht zu werden:
· frxUSD: Als Stablecoin für FRAX, 1:1 an den US-Dollar gekoppelt
· FraxNet: Eine Bankenschnittstelle, die entwickelt wurde, um das traditionelle Finanzsystem mit DeFi zu verbinden
· Fraxtal: Eine L2-Ausführungsschicht (oder eine allmähliche Umstellung auf L1), die effizienten Handel und Skalierbarkeit bietet
Die Token-Restrukturierung ist auch Teil der Zukunftspläne von FRAX. FXS wurde in FRAX umbenannt und mit Funktionen wie Gas, Governance, Burning und Staking ausgestattet. Diese Änderung zielt darauf ab, die Funktionalität und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit von FRAX zu verbessern und es dem Unternehmen zu ermöglichen, flexibler in einer konformen Umgebung zu arbeiten.
Wenn Sie FRAX als veFRAX einsetzen, können Sie potenzielle Belohnungen wie FXTL (Frax' eigene Punkte), Karak, Ethena und Symbiotic-Punkte erhalten.
Die Gründer betreiben aktiv und beteiligen sich an der Gesetzgebung im Zusammenhang mit Stablecoins, und ihre eigene Produkt-Roadmap wird aktiv an narrative Dienstleistungen angepasst. Mit der weiteren Umsetzung des GENIUS Act ist die Performance von FXS (FRAX) es wert, dass man sich darauf freut.
Link zum Originalartikel
Original anzeigen

6.962
0

Odaily
Originalartikel von Alex Liu, Foresight News
Der Stablecoin Act vs. FXS
Am 20. Mai wurde der GENIUS Act, ein Gesetzentwurf für Stablecoins in den Vereinigten Staaten, im Senat verabschiedet, und es sind noch zwei wichtige Schritte bis zur Abstimmung im Repräsentantenhaus und der Unterschrift des Präsidenten. Die Märkte glaubten zuvor, dass eine Abstimmung im Senat das größte Hindernis für die Verabschiedung des Gesetzes sei, und wenn es keine Überraschungen gebe, sei es nur eine Frage der Zeit, bis das Gesetz vollständig verabschiedet werde.
Welches Krypto-Projekt ist der größte Gewinner dieses legislativen Sieges? In Bezug auf die Wertentwicklung des Token-Preises könnte es Frax Finance sein.
Mit der Verabschiedung des Gesetzentwurfs im Senat stieg der Frax Finance-Token FXS (jetzt in FRAX umbenannt, der an den zentralisierten Börsen noch nicht aktualisiert wurde) kurzzeitig über 4,4 USDT und belegte damit den ersten Platz unter den Mainstream-Börsen. Selbst mit einer leichten Korrektur des Preises im Moment sind die FXS im Laufe des Monats immer noch um mehr als 100% gestiegen.
Warum ist das Gesetz gut für Frax Finance und warum wird Frax von einigen als der größte Gewinner des GENIUS Act angesehen?
Frax Finanzen
Bei den Produkten von Frax Finance handelt es sich nicht nur um Stablecoins, sondern auch um Liquid Staking, Lending, L2 und mehr. Aber sie haben tiefe Wurzeln in den Stablecoins. Frax war früher der Emittent des hybriden algorithmischen Stablecoins FRAX, gab aber nach dem Crash von Luna UST den "rechnerischen" Weg auf und wandelte sich in einen vollständig besicherten Stablecoin um.
Seitdem wurde FRAX weiter auf frxUSD aktualisiert, das durch Fiat-Währung gesichert ist, "mit der gesamten Roadmap, der erste lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin zu werden".
Frax-Gründer Sam deutete an, dass Frax am meisten von dem Gesetz profitiert habe
Aber warum wurde frxUSD der "erste" lizenzierte Fiat-Währungs-Stablecoin vor USDC, USDY und anderen Produkten? Auf regulatorischer Ebene hat es wirklich die Möglichkeit, "nah am Wasser zu sein und zuerst den ersten Monat zu bekommen".
Sam Kazemian, der Gründer von Frax Finance, hat seit Anfang des Jahres häufig Fotos von sich mit Krypto-Gesetzgebern in Washington, D.C., gepostet. Es wird gemunkelt, dass er als Brancheninsider stark in die Diskussion und Ausarbeitung des GENIUS Act involviert war. Der Markt scheint den regulatorischen Vorteil, den Frax Finance entsprechend haben wird, einzupreisen.
Sam posiert mit kryptofreundlichem Senator Lummis
Wenn die Spekulationen wahr sind, hat Sam als Verfasser und Teilnehmer des Gesetzentwurfs natürlich ein tieferes Verständnis für den GENIUS Act, und es ist für sein Projekt einfacher, die Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Darüber hinaus bleibt abzuwarten, ob die freundschaftlichen Beziehungen zum Gesetzgeber regulatorisch grünes Licht für die Zukunft von FRAX geben werden.
Der zukünftige Weg von FRAX
Zusätzlich zu den potenziellen regulatorischen Möglichkeiten baut FRAX ein vertikal integriertes Stablecoin-Ökosystem auf, das frxUSD (Stablecoin), FraxNet (Bankschnittstelle) und Fraxtal (L2 Execution Layer) umfasst, um den Anforderungen des zukünftigen regulatorischen Umfelds gerecht zu werden:
frxUSD: Als Stablecoin für FRAX, 1:1 an den US-Dollar gekoppelt.
FraxNet: Eine Banking-Schnittstelle, die entwickelt wurde, um das traditionelle Finanzsystem mit DeFi zu verbinden.
Fraxtal: Eine L2-Ausführungsschicht (oder eine allmähliche Umstellung auf L1), die effizienten Handel und Skalierbarkeit bietet.
Die Token-Restrukturierung ist auch Teil der Zukunftspläne von FRAX. FXS wurde in FRAX umbenannt und mit Funktionen wie Gas, Governance, Burning und Staking ausgestattet. Diese Änderung zielt darauf ab, die Funktionalität und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit von FRAX zu verbessern und es dem Unternehmen zu ermöglichen, flexibler in einer konformen Umgebung zu arbeiten.
Wenn Sie FRAX als veFRAX einsetzen, können Sie potenzielle Belohnungen wie FXTL (Frax' eigene Punkte), Karak, Ethena und Symbiotic-Punkte erhalten.
Die Gründer betreiben aktiv und beteiligen sich an der Gesetzgebung im Zusammenhang mit Stablecoins, und ihre eigene Produkt-Roadmap wird aktiv an narrative Dienstleistungen angepasst. Mit der weiteren Umsetzung des GENIUS Act ist die Performance von FXS (FRAX) es wert, dass man sich darauf freut.
Link zum Originalartikel
Original anzeigen

6.847
0
FXS-Rechner


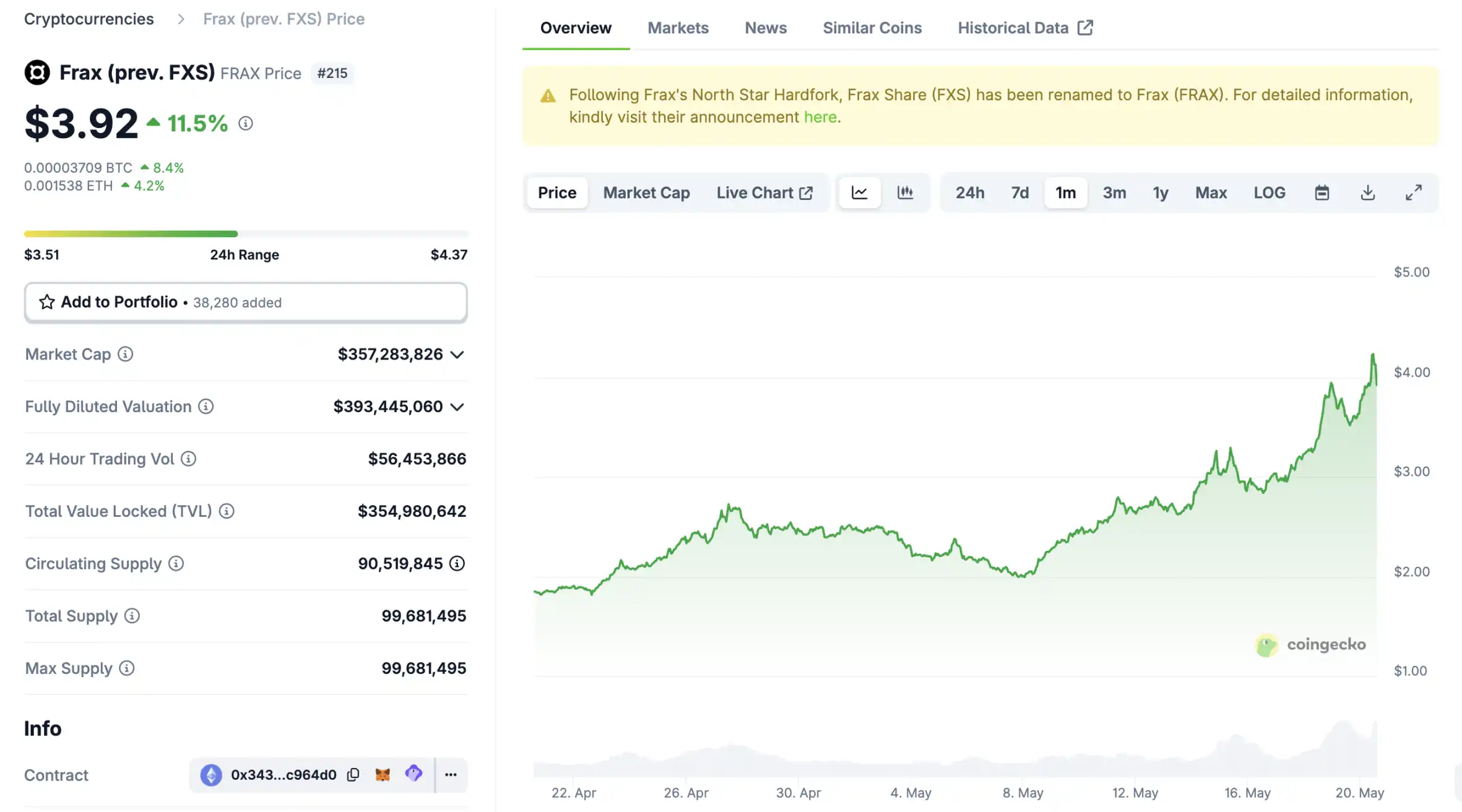
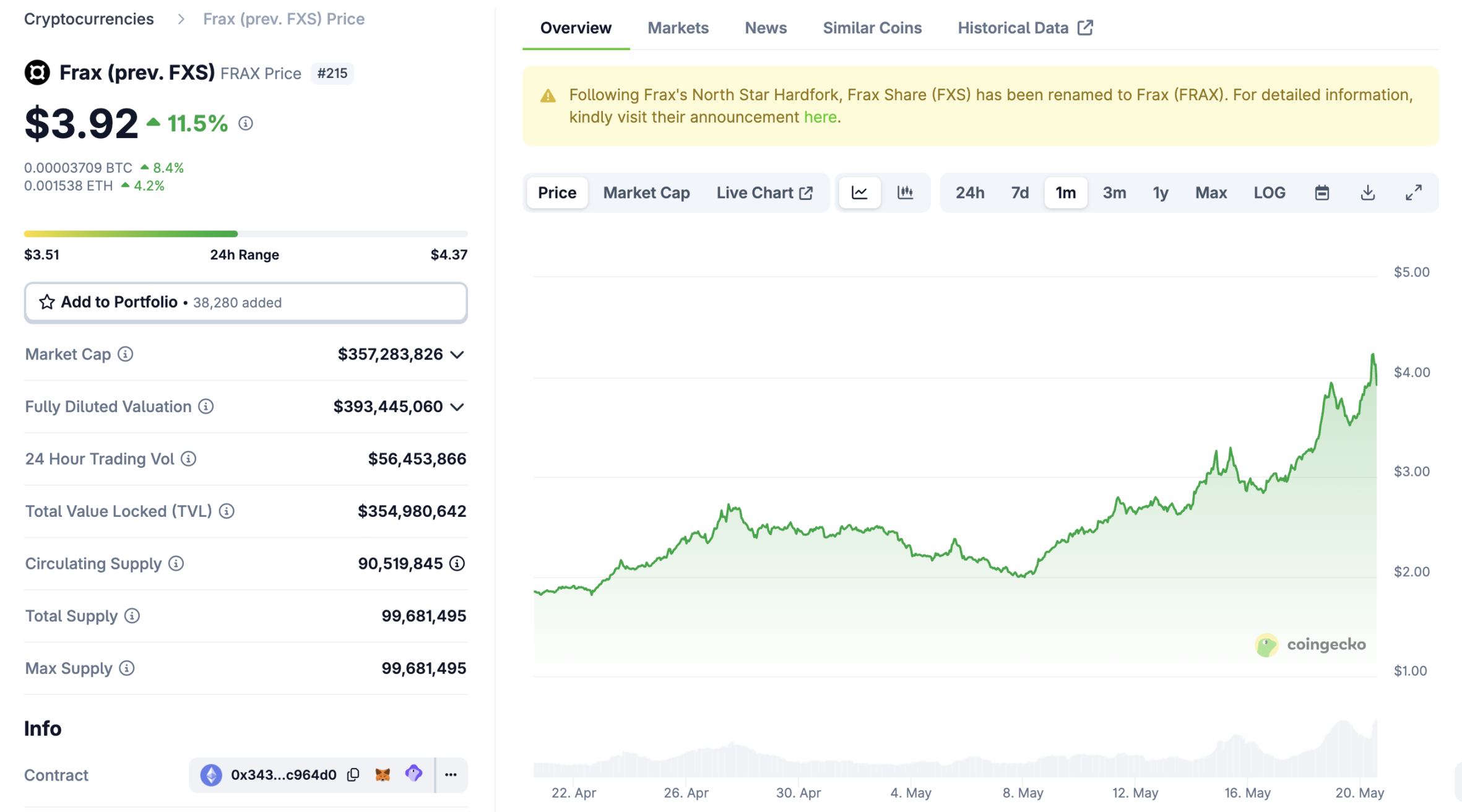
Frax Share Preisentwicklung in USD
Der aktuelle Preis von Frax Share liegt bei $3,7960. In den letzten 24 Stunden ist Frax Share um -0,91 % gesunken. Der Coin hat derzeit eine Umlaufmenge von 90.657.201 FXS und eine maximale Versorgung von 99.681.496 FXS, was eine vollständig verwässerte Marktkapitalisierung von $344,50M ergibt. In der Rangliste der Marktkapitalisierung belegt der Frax Share-Coin derzeit die Position 103. Der Frax Share/USD-Kurs wird in Echtzeit aktualisiert.
Heute
-$0,03500
-0,92 %
7 Tage
+$0,78400
+26,02 %
30 Tage
+$1,8890
+99,05 %
3 Monate
+$1,8900
+99,16 %
Beliebte Frax Share-Konvertierungen
Letzte Aktualisierung: 22.05.2025, 01:27
| 1 FXS in USD | 3,8000 $ |
| 1 FXS in EUR | 3,3502 € |
| 1 FXS in PHP | 211,28 ₱ |
| 1 FXS in IDR | 62.111,80 Rp |
| 1 FXS in GBP | 2,8263 £ |
| 1 FXS in CAD | 5,2529 $ |
| 1 FXS in AED | 13,9574 AED |
| 1 FXS in VND | 98.701,30 ₫ |
Über Frax Share (FXS)
Die angegebene Bewertung ist eine aggregierte Bewertung, die von OKX aus den angegebenen Quellen gesammelt wurde und nur zu Informationszwecken dient. OKX übernimmt keine Garantie für die Qualität oder Richtigkeit der Bewertungen. Es ist nicht beabsichtigt, (i) eine Anlageberatung oder -empfehlung, (ii) ein Angebot oder eine Aufforderung zum Kauf, Verkauf oder Halten von digitalen Vermögenswerten oder (iii) eine Finanz-, Buchhaltungs-, Rechts- oder Steuerberatung anzubieten. Digitale Vermögenswerte, einschließlich Stablecoins und NFTs, sind mit einem hohen Risiko behaftet, ihr Wert kann stark schwanken und sie können sogar wertlos werden. Der Preis und die Wertentwicklung der digitalen Vermögenswerte sind nicht garantiert und können sich ohne vorherige Ankündigung ändern. Ihre digitalen Vermögenswerte sind nicht durch eine Versicherung gegen mögliche Verluste abgedeckt. Historische Renditen sind kein Indikator für zukünftige Renditen. OKX garantiert keine Rendite, Rückzahlung von Kapital oder Zinsen. OKX gibt keine Anlage- oder Vermögensempfehlungen ab. Sie sollten sorgfältig abwägen, ob der Handel mit oder das Halten von digitalen Vermögenswerten angesichts Ihrer finanziellen Situation für Sie geeignet ist. Bitte konsultieren Sie Ihren Rechts-/Steuer-/Anlageexperten, wenn Sie Fragen bezüglich Ihrer individuellen Gegebenheiten haben.
Mehr anzeigen
- Offizielle Website
- Block Explorer
Über Websites von Drittanbietern
Über Websites von Drittanbietern
Durch die Nutzung der Website eines Drittanbieters (Third-Party Website, „TPW“) akzeptieren Sie, dass jegliche Nutzung der TPW den Bedingungen der TPW unterliegt und durch diese geregelt wird. Sofern nicht ausdrücklich schriftlich anders angegeben, stehen OKX und seine verbundenen Unternehmen („OKX“) in keiner Weise mit dem Eigentümer oder Betreiber der TPW in Verbindung. Sie erklären sich damit einverstanden, dass OKX nicht für Verluste, Schäden und sonstige Folgen haftet, die sich aus Ihrer Nutzung der TPW ergeben. Bitte beachten Sie, dass die Nutzung einer TPW zu einem Verlust oder einer Minderung Ihres Vermögens führen kann.
Häufig gestellte Fragen zum Frax Share-Preis
Wie viel ist 1 Frax Share heute wert?
Aktuell ist ein Frax Share $3,7960 wert. Wenn Sie Antworten und Einblicke in das Preisgeschehen von Frax Share suchen, sind Sie hier genau an der richtigen Stelle. Entdecken Sie die neuesten Frax Share-Charts und handeln Sie verantwortungsbewusst mit OKX.
Was ist eine Kryptowährung?
Kryptowährungen, wie etwa Frax Share, sind digitale Vermögenswerte, die auf einem öffentlichen Hauptbuch namens Blockchains betrieben werden. Erfahren Sie mehr über die auf OKX angebotenen Coins und Tokens sowie deren unterschiedlichen Eigenschaften, einschließlich Live-Preisen und Charts in Echtzeit.
Wann wurden Kryptowährungen erfunden?
Dank der Finanzkrise von 2008 ist das Interesse an einem dezentralen Finanzwesen rasant gestiegen. Bitcoin bot als sicherer digitaler Vermögenswert auf einem dezentralen Netzwerk eine neuartige Lösung. Seitdem wurden auch viele andere Token, wie etwa Frax Share, erstellt.
Wird der Preis von Frax Share heute steigen?
Auf unserer Frax Share-Seite für Preisprognosen finden Sie Prognosen zukünftiger Preise und können Ihre Preisziele bestimmen.
ESG-Offenlegung
ESG-Regulierungen (Umwelt, Soziales und Governance) für Krypto-Vermögenswerte zielen darauf ab, ihre Umweltauswirkungen (z. B. energieintensives Mining) zu adressieren, Transparenz zu fördern und ethische Governance-Praktiken zu gewährleisten, um die Krypto-Industrie mit breiteren Nachhaltigkeits- und gesellschaftlichen Zielen in Einklang zu bringen. Diese Vorschriften fördern die Compliance mit Standards, die Risiken mindern und das Vertrauen in digitale Vermögenswerte stärken.
Details zum Vermögenswert
Name
OKcoin Europe LTD
Kennung der relevanten juristischen Person
54930069NLWEIGLHXU42
Name des Krypto-Vermögenswerts
Frax Share
Konsensmechanismus
Frax Share is present on the following networks: arbitrum, avalanche, binance_smart_chain, ethereum, fantom, solana.
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 solution on top of Ethereum that uses Optimistic Rollups to enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs. It assumes that transactions are valid by default and only verifies them if there's a challenge (optimistic): Core Components: • Sequencer: Orders transactions and creates batches for processing. • Bridge: Facilitates asset transfers between Arbitrum and Ethereum. • Fraud Proofs: Protect against invalid transactions through an interactive verification process. Verification Process: 1. Transaction Submission: Users submit transactions to the Arbitrum Sequencer, which orders and batches them. 2. State Commitment: These batches are submitted to Ethereum with a state commitment. 3. Challenge Period: Validators have a specific period to challenge the state if they suspect fraud. 4. Dispute Resolution: If a challenge occurs, the dispute is resolved through an iterative process to identify the fraudulent transaction. The final operation is executed on Ethereum to determine the correct state. 5. Rollback and Penalties: If fraud is proven, the state is rolled back, and the dishonest party is penalized. Security and Efficiency: The combination of the Sequencer, bridge, and interactive fraud proofs ensures that the system remains secure and efficient. By minimizing on-chain data and leveraging off-chain computations, Arbitrum can provide high throughput and low fees.
The Avalanche blockchain network employs a unique Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism called Avalanche Consensus, which involves three interconnected protocols: Snowball, Snowflake, and Avalanche. Avalanche Consensus Process 1. Snowball Protocol: o Random Sampling: Each validator randomly samples a small, constant-sized subset of other validators. Repeated Polling: Validators repeatedly poll the sampled validators to determine the preferred transaction. Confidence Counters: Validators maintain confidence counters for each transaction, incrementing them each time a sampled validator supports their preferred transaction. Decision Threshold: Once the confidence counter exceeds a pre-defined threshold, the transaction is considered accepted. 2. Snowflake Protocol: Binary Decision: Enhances the Snowball protocol by incorporating a binary decision process. Validators decide between two conflicting transactions. Binary Confidence: Confidence counters are used to track the preferred binary decision. Finality: When a binary decision reaches a certain confidence level, it becomes final. 3. Avalanche Protocol: DAG Structure: Uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure to organize transactions, allowing for parallel processing and higher throughput. Transaction Ordering: Transactions are added to the DAG based on their dependencies, ensuring a consistent order. Consensus on DAG: While most Proof-of-Stake Protocols use a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus, Avalanche uses the Avalanche Consensus, Validators reach consensus on the structure and contents of the DAG through repeated Snowball and Snowflake.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses a hybrid consensus mechanism called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which combines elements of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA). This method ensures fast block times and low fees while maintaining a level of decentralization and security. Core Components 1. Validators (so-called “Cabinet Members”): Validators on BSC are responsible for producing new blocks, validating transactions, and maintaining the network’s security. To become a validator, an entity must stake a significant amount of BNB (Binance Coin). Validators are selected through staking and voting by token holders. There are 21 active validators at any given time, rotating to ensure decentralization and security. 2. Delegators: Token holders who do not wish to run validator nodes can delegate their BNB tokens to validators. This delegation helps validators increase their stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Delegators earn a share of the rewards that validators receive, incentivizing broad participation in network security. 3. Candidates: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are in the pool waiting to become validators. They are essentially potential validators who are not currently active but can be elected to the validator set through community voting. Candidates play a crucial role in ensuring there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, thus maintaining network resilience and decentralization. Consensus Process 4. Validator Selection: Validators are chosen based on the amount of BNB staked and votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. The selection process involves both the current validators and the pool of candidates, ensuring a dynamic and secure rotation of nodes. 5. Block Production: The selected validators take turns producing blocks in a PoA-like manner, ensuring that blocks are generated quickly and efficiently. Validators validate transactions, add them to new blocks, and broadcast these blocks to the network. 6. Transaction Finality: BSC achieves fast block times of around 3 seconds and quick transaction finality. This is achieved through the efficient PoSA mechanism that allows validators to rapidly reach consensus. Security and Economic Incentives 7. Staking: Validators are required to stake a substantial amount of BNB, which acts as collateral to ensure their honest behavior. This staked amount can be slashed if validators act maliciously. Staking incentivizes validators to act in the network's best interest to avoid losing their staked BNB. 8. Delegation and Rewards: Delegators earn rewards proportional to their stake in validators. This incentivizes them to choose reliable validators and participate in the network’s security. Validators and delegators share transaction fees as rewards, which provides continuous economic incentives to maintain network security and performance. 9. Transaction Fees: BSC employs low transaction fees, paid in BNB, making it cost-effective for users. These fees are collected by validators as part of their rewards, further incentivizing them to validate transactions accurately and efficiently.
The Ethereum network uses a Proof-of-Stake Consensus Mechanism to validate new transactions on the blockchain. Core Components 1. Validators: Validators are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To become a validator, a user must deposit (stake) 32 ETH into a smart contract. This stake acts as collateral and can be slashed if the validator behaves dishonestly. 2. Beacon Chain: The Beacon Chain is the backbone of Ethereum 2.0. It coordinates the network of validators and manages the consensus protocol. It is responsible for creating new blocks, organizing validators into committees, and implementing the finality of blocks. Consensus Process 1. Block Proposal: Validators are chosen randomly to propose new blocks. This selection is based on a weighted random function (WRF), where the weight is determined by the amount of ETH staked. 2. Attestation: Validators not proposing a block participate in attestation. They attest to the validity of the proposed block by voting for it. Attestations are then aggregated to form a single proof of the block’s validity. 3. Committees: Validators are organized into committees to streamline the validation process. Each committee is responsible for validating blocks within a specific shard or the Beacon Chain itself. This ensures decentralization and security, as a smaller group of validators can quickly reach consensus. 4. Finality: Ethereum 2.0 uses a mechanism called Casper FFG (Friendly Finality Gadget) to achieve finality. Finality means that a block and its transactions are considered irreversible and confirmed. Validators vote on the finality of blocks, and once a supermajority is reached, the block is finalized. 5. Incentives and Penalties: Validators earn rewards for participating in the network, including proposing blocks and attesting to their validity. Conversely, validators can be penalized (slashed) for malicious behavior, such as double-signing or being offline for extended periods. This ensures honest participation and network security.
Fantom operates on the Lachesis Protocol, an Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) consensus mechanism designed for fast, secure, and scalable transactions. Core Components of Fantom’s Consensus: 1. Lachesis Protocol (aBFT): Asynchronous and Leaderless: Lachesis allows nodes to reach consensus independently without relying on a central leader, enhancing decentralization and speed. DAG Structure: Instead of a linear blockchain, Lachesis uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, allowing multiple transactions to be processed in parallel across nodes. This structure supports high throughput, making the network suitable for applications requiring rapid transaction processing. 2. Event Blocks and Instant Finality: Event Blocks: Transactions are grouped into event blocks, which are validated asynchronously by multiple validators. When enough validators confirm an event block, it becomes part of the Fantom network’s history. Instant Finality: Transactions on Fantom achieve immediate finality, meaning they are confirmed and cannot be reversed. This property is ideal for applications requiring fast and irreversible transactions.
Solana uses a unique combination of Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to achieve high throughput, low latency, and robust security. Here’s a detailed explanation of how these mechanisms work: Core Concepts 1. Proof of History (PoH): Time-Stamped Transactions: PoH is a cryptographic technique that timestamps transactions, creating a historical record that proves that an event has occurred at a specific moment in time. Verifiable Delay Function: PoH uses a Verifiable Delay Function (VDF) to generate a unique hash that includes the transaction and the time it was processed. This sequence of hashes provides a verifiable order of events, enabling the network to efficiently agree on the sequence of transactions. 2. Proof of Stake (PoS): Validator Selection: Validators are chosen to produce new blocks based on the number of SOL tokens they have staked. The more tokens staked, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. Delegation: Token holders can delegate their SOL tokens to validators, earning rewards proportional to their stake while enhancing the network's security. Consensus Process 1. Transaction Validation: Transactions are broadcast to the network and collected by validators. Each transaction is validated to ensure it meets the network’s criteria, such as having correct signatures and sufficient funds. 2. PoH Sequence Generation: A validator generates a sequence of hashes using PoH, each containing a timestamp and the previous hash. This process creates a historical record of transactions, establishing a cryptographic clock for the network. 3. Block Production: The network uses PoS to select a leader validator based on their stake. The leader is responsible for bundling the validated transactions into a block. The leader validator uses the PoH sequence to order transactions within the block, ensuring that all transactions are processed in the correct order. 4. Consensus and Finalization: Other validators verify the block produced by the leader validator. They check the correctness of the PoH sequence and validate the transactions within the block. Once the block is verified, it is added to the blockchain. Validators sign off on the block, and it is considered finalized. Security and Economic Incentives 1. Incentives for Validators: Block Rewards: Validators earn rewards for producing and validating blocks. These rewards are distributed in SOL tokens and are proportional to the validator’s stake and performance. Transaction Fees: Validators also earn transaction fees from the transactions included in the blocks they produce. These fees provide an additional incentive for validators to process transactions efficiently. 2. Security: Staking: Validators must stake SOL tokens to participate in the consensus process. This staking acts as collateral, incentivizing validators to act honestly. If a validator behaves maliciously or fails to perform, they risk losing their staked tokens. Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their SOL tokens to validators, enhancing network security and decentralization. Delegators share in the rewards and are incentivized to choose reliable validators. 3. Economic Penalties: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior, such as double-signing or producing invalid blocks. This penalty, known as slashing, results in the loss of a portion of the staked tokens, discouraging dishonest actions.
Anreizmechanismen und anfallende Gebühren
Frax Share is present on the following networks: arbitrum, avalanche, binance_smart_chain, ethereum, fantom, solana.
Arbitrum One, a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, employs several incentive mechanisms to ensure the security and integrity of transactions on its network. The key mechanisms include: 1. Validators and Sequencers: o Sequencers are responsible for ordering transactions and creating batches that are processed off-chain. They play a critical role in maintaining the efficiency and throughput of the network. o Validators monitor the sequencers' actions and ensure that transactions are processed correctly. Validators verify the state transitions and ensure that no invalid transactions are included in the batches. 2. Fraud Proofs: o Assumption of Validity: Transactions processed off-chain are assumed to be valid. This allows for quick transaction finality and high throughput. o Challenge Period: There is a predefined period during which anyone can challenge the validity of a transaction by submitting a fraud proof. This mechanism acts as a deterrent against malicious behavior. o Dispute Resolution: If a challenge is raised, an interactive verification process is initiated to pinpoint the exact step where fraud occurred. If the challenge is valid, the fraudulent transaction is reverted, and the dishonest actor is penalized. 3. Economic Incentives: o Rewards for Honest Behavior: Participants in the network, such as validators and sequencers, are incentivized through rewards for performing their duties honestly and efficiently. These rewards come from transaction fees and potentially other protocol incentives. o Penalties for Malicious Behavior: Participants who engage in dishonest behavior or submit invalid transactions are penalized. This can include slashing of staked tokens or other forms of economic penalties, which serve to discourage malicious actions. Fees on the Arbitrum One Blockchain 1. Transaction Fees: o Layer 2 Fees: Users pay fees for transactions processed on the Layer 2 network. These fees are typically lower than Ethereum mainnet fees due to the reduced computational load on the main chain. o Arbitrum Transaction Fee: A fee is charged for each transaction processed by the sequencer. This fee covers the cost of processing the transaction and ensuring its inclusion in a batch. 2. L1 Data Fees: o Posting Batches to Ethereum: Periodically, the state updates from the Layer 2 transactions are posted to the Ethereum mainnet as calldata. This involves a fee, known as the L1 data fee, which accounts for the gas required to publish these state updates on Ethereum. o Cost Sharing: Because transactions are batched, the fixed costs of posting state updates to Ethereum are spread across multiple transactions, making it more cost-effective for users.
Avalanche uses a consensus mechanism known as Avalanche Consensus, which relies on a combination of validators, staking, and a novel approach to consensus to ensure the network's security and integrity. Validators: Staking: Validators on the Avalanche network are required to stake AVAX tokens. The amount staked influences their probability of being selected to propose or validate new blocks. Rewards: Validators earn rewards for their participation in the consensus process. These rewards are proportional to the amount of AVAX staked and their uptime and performance in validating transactions. Delegation: Validators can also accept delegations from other token holders. Delegators share in the rewards based on the amount they delegate, which incentivizes smaller holders to participate indirectly in securing the network. 2. Economic Incentives: Block Rewards: Validators receive block rewards for proposing and validating blocks. These rewards are distributed from the network’s inflationary issuance of AVAX tokens. Transaction Fees: Validators also earn a portion of the transaction fees paid by users. This includes fees for simple transactions, smart contract interactions, and the creation of new assets on the network. 3. Penalties: Slashing: Unlike some other PoS systems, Avalanche does not employ slashing (i.e., the confiscation of staked tokens) as a penalty for misbehavior. Instead, the network relies on the financial disincentive of lost future rewards for validators who are not consistently online or act maliciously. o Uptime Requirements: Validators must maintain a high level of uptime and correctly validate transactions to continue earning rewards. Poor performance or malicious actions result in missed rewards, providing a strong economic incentive to act honestly. Fees on the Avalanche Blockchain 1. Transaction Fees: Dynamic Fees: Transaction fees on Avalanche are dynamic, varying based on network demand and the complexity of the transactions. This ensures that fees remain fair and proportional to the network's usage. Fee Burning: A portion of the transaction fees is burned, permanently removing them from circulation. This deflationary mechanism helps to balance the inflation from block rewards and incentivizes token holders by potentially increasing the value of AVAX over time. 2. Smart Contract Fees: Execution Costs: Fees for deploying and interacting with smart contracts are determined by the computational resources required. These fees ensure that the network remains efficient and that resources are used responsibly. 3. Asset Creation Fees: New Asset Creation: There are fees associated with creating new assets (tokens) on the Avalanche network. These fees help to prevent spam and ensure that only serious projects use the network's resources.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism to ensure network security and incentivize participation from validators and delegators. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators must stake a significant amount of BNB to participate in the consensus process. They earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and block rewards. Selection Process: Validators are selected based on the amount of BNB staked and the votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. 2. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their BNB to validators. This delegation increases the validator's total stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Shared Rewards: Delegators earn a portion of the rewards that validators receive. This incentivizes token holders to participate in the network’s security and decentralization by choosing reliable validators. 3. Candidates: Pool of Potential Validators: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are waiting to become active validators. They ensure that there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, maintaining network resilience. 4. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior or failure to perform their duties. Penalties include slashing a portion of their staked tokens, ensuring that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: Staking requires validators and delegators to lock up their BNB tokens, providing an economic incentive to act honestly to avoid losing their staked assets. Fees on the Binance Smart Chain 5. Transaction Fees: Low Fees: BSC is known for its low transaction fees compared to other blockchain networks. These fees are paid in BNB and are essential for maintaining network operations and compensating validators. Dynamic Fee Structure: Transaction fees can vary based on network congestion and the complexity of the transactions. However, BSC ensures that fees remain significantly lower than those on the Ethereum mainnet. 6. Block Rewards: Incentivizing Validators: Validators earn block rewards in addition to transaction fees. These rewards are distributed to validators for their role in maintaining the network and processing transactions. 7. Cross-Chain Fees: Interoperability Costs: BSC supports cross-chain compatibility, allowing assets to be transferred between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain. These cross-chain operations incur minimal fees, facilitating seamless asset transfers and improving user experience. 8. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Execution Costs: Deploying and interacting with smart contracts on BSC involves paying fees based on the computational resources required. These fees are also paid in BNB and are designed to be cost-effective, encouraging developers to build on the BSC platform.
Ethereum, particularly after transitioning to Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2), employs a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to secure its network. The incentives for validators and the fee structures play crucial roles in maintaining the security and efficiency of the blockchain. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Staking Rewards: Validator Rewards: Validators are essential to the PoS mechanism. They are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To participate, they must stake a minimum of 32 ETH. In return, they earn rewards for their contributions, which are paid out in ETH. These rewards are a combination of newly minted ETH and transaction fees from the blocks they validate. Reward Rate: The reward rate for validators is dynamic and depends on the total amount of ETH staked in the network. The more ETH staked, the lower the individual reward rate, and vice versa. This is designed to balance the network's security and the incentive to participate. 2. Transaction Fees: Base Fee: After the implementation of Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 1559, the transaction fee model changed to include a base fee that is burned (i.e., removed from circulation). This base fee adjusts dynamically based on network demand, aiming to stabilize transaction fees and reduce volatility. Priority Fee (Tip): Users can also include a priority fee (tip) to incentivize validators to include their transactions more quickly. This fee goes directly to the validators, providing them with an additional incentive to process transactions efficiently. 3. Penalties for Malicious Behavior: Slashing: Validators face penalties (slashing) if they engage in malicious behavior, such as double-signing or validating incorrect information. Slashing results in the loss of a portion of their staked ETH, discouraging bad actors and ensuring that validators act in the network's best interest. Inactivity Penalties: Validators also face penalties for prolonged inactivity. This ensures that validators remain active and engaged in maintaining the network's security and operation. Fees Applicable on the Ethereum Blockchain 1. Gas Fees: Calculation: Gas fees are calculated based on the computational complexity of transactions and smart contract executions. Each operation on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has an associated gas cost. Dynamic Adjustment: The base fee introduced by EIP-1559 dynamically adjusts according to network congestion. When demand for block space is high, the base fee increases, and when demand is low, it decreases. 2. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Interaction: Deploying a smart contract on Ethereum involves paying gas fees proportional to the contract's complexity and size. Interacting with deployed smart contracts (e.g., executing functions, transferring tokens) also incurs gas fees. Optimizations: Developers are incentivized to optimize their smart contracts to minimize gas usage, making transactions more cost-effective for users. 3. Asset Transfer Fees: Token Transfers: Transferring ERC-20 or other token standards involves gas fees. These fees vary based on the token's contract implementation and the current network demand.
Fantom’s incentive model promotes network security through staking rewards, transaction fees, and delegation options, encouraging broad participation. Incentive Mechanisms: 1. Staking Rewards for Validators: Earning Rewards in FTM: Validators who participate in the consensus process earn rewards in FTM tokens, proportional to the amount they have staked. This incentivizes validators to actively secure the network. Dynamic Staking Rate: Fantom’s staking reward rate is dynamic, adjusting based on total FTM staked across the network. As more FTM is staked, individual rewards may decrease, maintaining a balanced reward structure that supports long-term network security. 2. Delegation for Token Holders: Delegated Staking: Users who do not operate validator nodes can delegate their FTM tokens to validators. In return, they share in the staking rewards, encouraging wider participation in securing the network. Applicable Fees: • Transaction Fees in FTM: Users pay transaction fees in FTM tokens. The network’s high throughput and DAG structure keep fees low, making Fantom ideal for decentralized applications (dApps) requiring frequent transactions. • Efficient Fee Model: The low fees and scalability of the network make it cost-effective for users, fostering a favorable environment for high-volume applications.
Solana uses a combination of Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to secure its network and validate transactions. Here’s a detailed explanation of the incentive mechanisms and applicable fees: Incentive Mechanisms 4. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators are chosen based on the number of SOL tokens they have staked. They earn rewards for producing and validating blocks, which are distributed in SOL. The more tokens staked, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. Transaction Fees: Validators earn a portion of the transaction fees paid by users for the transactions they include in the blocks. This provides an additional financial incentive for validators to process transactions efficiently and maintain the network's integrity. 5. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders who do not wish to run a validator node can delegate their SOL tokens to a validator. In return, delegators share in the rewards earned by the validators. This encourages widespread participation in securing the network and ensures decentralization. 6. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior, such as producing invalid blocks or being frequently offline. This penalty, known as slashing, involves the loss of a portion of their staked tokens. Slashing deters dishonest actions and ensures that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: By staking SOL tokens, validators and delegators lock up their tokens, which could otherwise be used or sold. This opportunity cost incentivizes participants to act honestly to earn rewards and avoid penalties. Fees Applicable on the Solana Blockchain 7. Transaction Fees: Low and Predictable Fees: Solana is designed to handle a high throughput of transactions, which helps keep fees low and predictable. The average transaction fee on Solana is significantly lower compared to other blockchains like Ethereum. Fee Structure: Fees are paid in SOL and are used to compensate validators for the resources they expend to process transactions. This includes computational power and network bandwidth. 8. Rent Fees: State Storage: Solana charges rent fees for storing data on the blockchain. These fees are designed to discourage inefficient use of state storage and encourage developers to clean up unused state. Rent fees help maintain the efficiency and performance of the network. 9. Smart Contract Fees: Execution Costs: Similar to transaction fees, fees for deploying and interacting with smart contracts on Solana are based on the computational resources required. This ensures that users are charged proportionally for the resources they consume.
Beginn des Zeitraums, auf die sich die Angaben beziehen
2024-04-20
Ende des Zeitraums, auf die sich die Angaben beziehen
2025-04-20
Energiebericht
Energieverbrauch
955.61975 (kWh/a)
Quellen und Verfahren im Bezug auf den Energieverbrauch
The energy consumption of this asset is aggregated across multiple components:
To determine the energy consumption of a token, the energy consumption of the network(s) arbitrum, avalanche, binance_smart_chain, ethereum, fantom, solana is calculated first. Based on the crypto asset's gas consumption per network, the share of the total consumption of the respective network that is assigned to this asset is defined. When calculating the energy consumption, we used - if available - the Functionally Fungible Group Digital Token Identifier (FFG DTI) to determine all implementations of the asset of question in scope and we update the mappings regulary, based on data of the Digital Token Identifier Foundation.
FXS-Rechner













